CHANNELS

Dr. Sebastian Brähler
+49 221 478-97672
sebastian.braehler@uk-koeln.de
TEAM MEMBERS
Paul Diefenhardt (Postdoc)
Bastian Trinsch
Sebastian Brähler
Inflammatory cells and glomerular injury
Immunobiology of glomerular diseases
Inflammatory diseases of the kidney filtering units (glomeruli) are a leading cause of chronic renal insufficiency. Despite tremendous advances in our disease understanding, the treatment options remain limited, therefore the investigation of inflammatory processes is of key importance for the development of targeted treatment strategies.
The kidney contains a dense network of immune cells, which is of central importance for organ homeostasis but can also lead to tissue damage and ultimately renal failure. While both kidney biology and renal immunology have made tremendous progress in the past, the interaction between kidney cells like tubulus cells or podocytes and immune cells is still poorly understood.
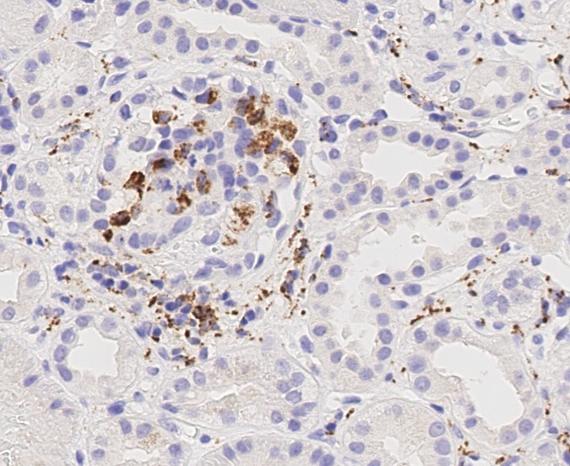
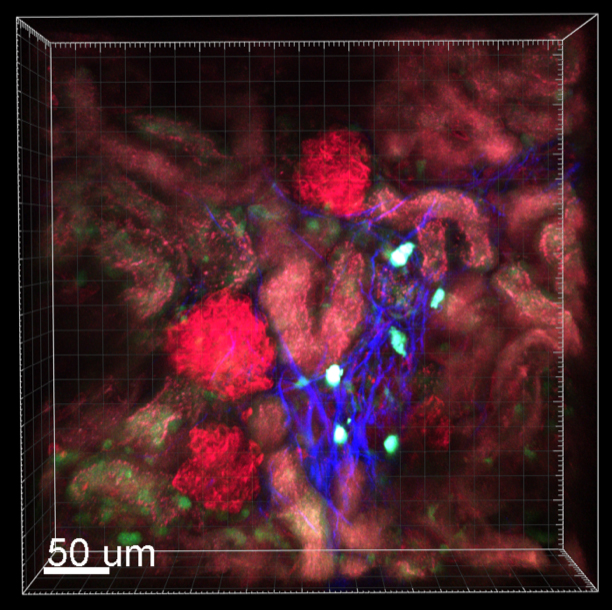
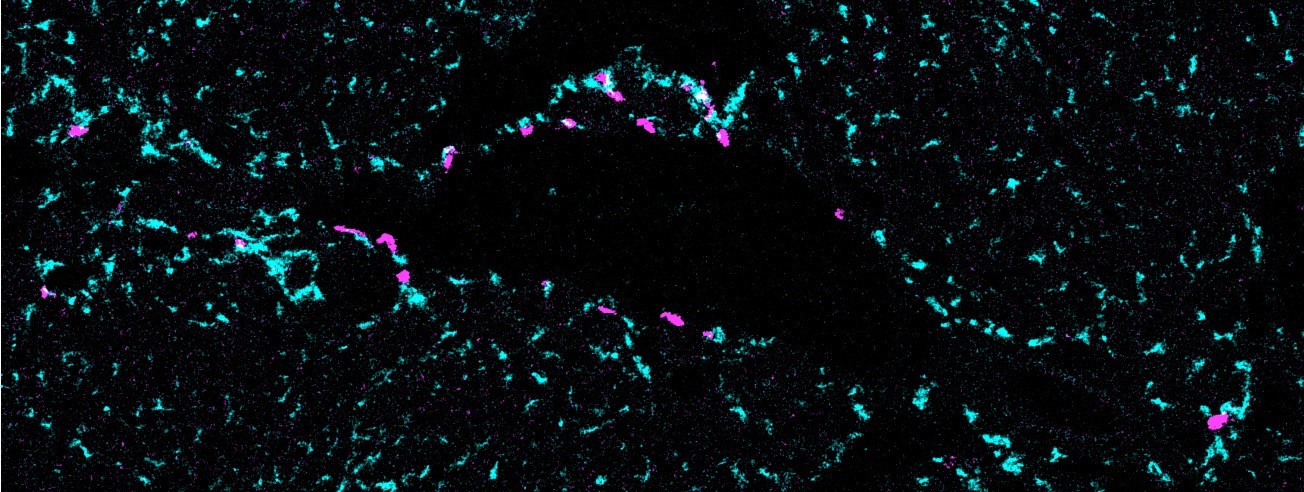
In the past our group has investigated the proinflammatory properties of podocytes in glomerulonephritis. We are using state-of-the-art live imaging to visualize disease processes and the dynamics of immune cell recruitment to kidney in real-time. Recently, we were able to redefine the function of cDC1 and cDC2 dendritic cells in glomerulonephrits. cDC2, which represent about 90% of DCs in the kidney, have a strong pro-inflammatory function during GN by recruiting Th17 through IL23 and secreting neutrophil-attracting cytokines. In contrast, the cDC1 subset had a robust anti-inflammatory function by counteracting the activity of the cDC2.
We are currently investigating the following areas:
- Characterization of the anti-inflammatory properties of cDC1: Based on our recent data, cDC1 have robust anti-inflammatory properties in glomerulonephritis. Therefore, we use kidney disease models, flow cytometry and advanced imaging methods to understand their exact molecular function.
- Analysis of glomerular pro-inflammatory signaling: Glomerulonephritis is a specific inflammation of the renal filtering unit. Renal cells like podocytes are among the first responders to tissue injury. We analyze and try to modulate the inflammatory environment in glomeruli to prevent disease progression right where it starts.
- Immune cell metabolism in renal diseases. Metabolism is a fundamental prerequisite for each cell’s activation and function. Our aim is to investigate the involvement of key metabolic pathways in renal disease like the TCA cycle.
SELECTED PUBLICATIONS
Viehmann, S.F., Bohner, A.M.C., Kurts, C., and Brahler, S. (2018) The multifaceted role of the renal mononuclear phagocyte system. Cell Immunol, 330: 97-104.
Brahler, S., Zinselmeyer, B.H., Raju, S., Nitschke, M., Suleiman, H., Saunders, B.T., Johnson, M.W., Bohner, A.M.C., Viehmann, S.F., Theisen, D.J., Kretzer, N.M., Briseno, C.G., Zaitsev, K., Ornatsky, O., Chang, Q., Carrero, J.A., Kopp, J.B., Artyomov, M.N., Kurts, C., Murphy, K.M., Miner, J.H., and Shaw, A.S. (2018) Opposing Roles of Dendritic Cell Subsets in Experimental GN. J Am Soc Nephrol, 29(1): 138-154.
Yu, H., Artomov, M., Brahler, S., Stander, M.C., Shamsan, G., Sampson, M.G., White, J.M., Kretzler, M., Miner, J.H., Jain, S., Winkler, C.A., Mitra, R.D., Kopp, J.B., Daly, M.J., and Shaw, A.S. (2016) A role for genetic susceptibility in sporadic focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. J Clin Invest, 126(4): 1603.
Brahler, S., Yu, H., Suleiman, H., Krishnan, G.M., Saunders, B.T., Kopp, J.B., Miner, J.H., Zinselmeyer, B.H., and Shaw, A.S. (2016) Intravital and Kidney Slice Imaging of Podocyte Membrane Dynamics. J Am Soc Nephrol, 27(11): 3285-3290.
Brahler, S., Ising, C., Barrera Aranda, B., Hohne, M., Schermer, B., Benzing, T., and Brinkkoetter, P.T. (2015) The NF-kappaB essential modulator (NEMO) controls podocyte cytoskeletal dynamics independently of NF-kappaB. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 309(7): F617-26.
